DataSource JMS
The JMS DataSource (Java Message Service) facilitates message transmission and reception to queues and topics across any message service conforming to the JMS specification. JMS serves as a widely adopted API for message-oriented middleware, allowing loosely coupled, reliable, and asynchronous communication between various components of distributed applications
Practical Scenarios for Using the DataSource
The JMS DataSource allows you to
-
Listen for new messages as they arrive at a specified destination.
-
Publish a new message and send it to a specified destination.
-
Consume a message at any given time in the flow from any given specified destination.
-
Publish a message to any specified destination, and then consume a reply on a different specified destination
JMS supports two models for messaging:
Point-to-point queues
Within the point-to-point queuing model, a sender dispatches messages to a specific queue, and a receiver retrieves those messages from the identical queue. In this framework, the sender possesses the knowledge of the message's destination and delivers the message directly to that destination.
-
Only one receiver consumes the received message.
-
The sender does not need to be running at the time the receiver consumes the message, and the receiver does not need to be running at the time the message is sent.
-
Every message that is successfully processed is acknowledged by the receiver.
Publish and subscribe topics
The publish and subscribe model allows a sender to publish messages to a specific message topic instead of a particular queue. Receivers subscribe to receive messages from a designated message topic. In this model, neither the sender nor the receiver has awareness of each other. A suitable analogy for this concept is an anonymous bulletin board.
-
Multiple receivers consume the receive the message, including none if there are no subscribers to the topic.
-
The sender must create a message topic in such a way that receivers can subscribe to that topic.
-
The receiver must remain continuously active to consume the receive messages, unless it has established a durable subscription in which case messages sent while the receiver is not connected are redistributed when the receiver reconnects.
Engaging in Practical Implementation
Open new Project in QuickIntegration Platform, and then follow these steps to get your flow working
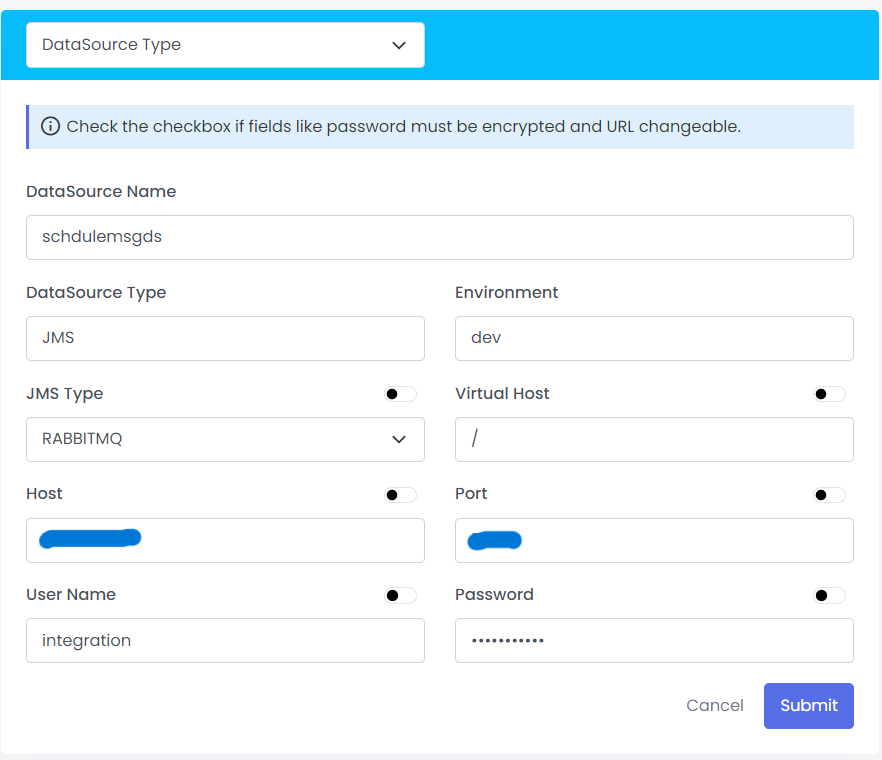
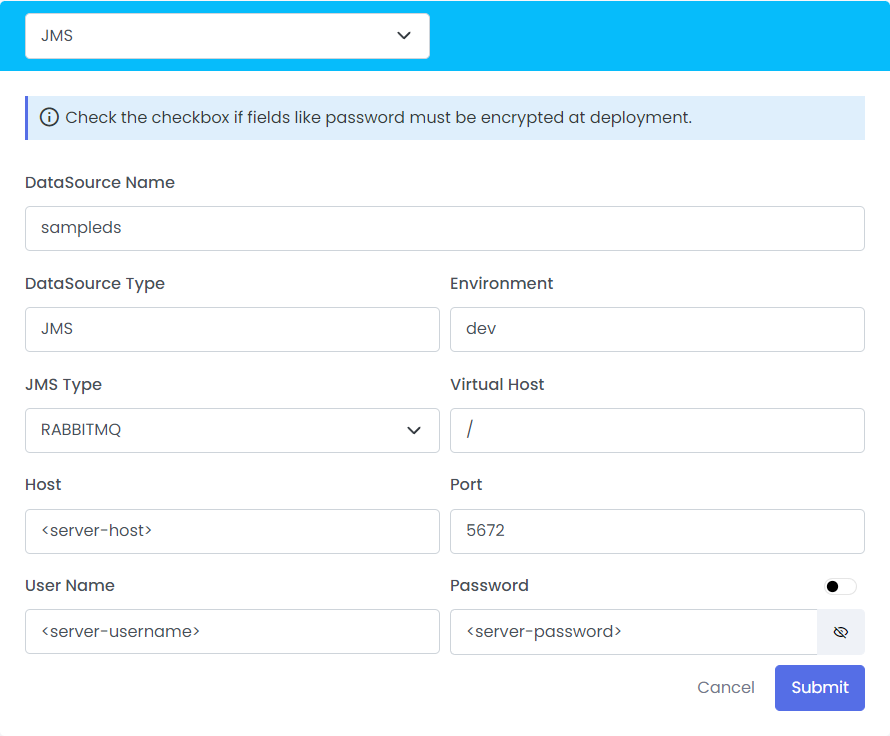
- Click On the Connection Properties
- Select the DataSource Type from drop down
- Provide the Credentials
- Click on Submit to save the Credentials
- On the left side of the palette, you'll find the Configured Properties ready to be utilized within your API.
 ;
;
 ;
;
| Fields | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| DataSource Name | Datasource Name which is configured in connections properties | schdulemsgds |
| DataSource Type | JMS | JMS |
| Environment | Provides a production environment where you can deploy applications and APIs publicly | dev |
| JMS Type | RABBITMQ/ACTIVEMQ | RABBITMQ |
| Virtual Host | / | |
| Host | A hostname is a domain name assigned to a host computer | abcd |
| Port | A port is a virtual point where network connections start and end. | 123 |
| User Name | A name that uses for identification purposes when logging | integration |
| Password | A password is a string of characters used to verify the identity of a user during the authentication process | abcd |